Stay updated with the latest cybersecurity news, covering recent threats, data breaches, and advancements in online security to protect businesses and individuals in 2024
What is Cybersecurity and how to save from us
Cybersecurity is defined as the discipline focused on
safeguarding systems, networks, devices, and information from digital threats,
unauthorized access, or harm. Such cyber threats typically seek to gain access
to, alter, or eliminate sensitive data, extort financial resources from
individuals, or disrupt standard business operations. The field of
cybersecurity encompasses a range of methods, strategies, and tools aimed at
protecting against these risks.
Network
Security: Protecting the Integrity of Networks from Unauthorized Access and
Attacks
Network Security: Safeguarding Network Integrity Against Unauthorized Access and Attacks Network security encompasses the methodologies and technologies employed to protect the framework of a network, which includes the devices, data, and users associated with it. The primary objective is to defend the network against unauthorized access, cyber threats, and various risks that may jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network and its information. Essential Components of Network Security: Firewalls A firewall serves as a protective barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet.
It regulates incoming and outgoing traffic according to established security protocols. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) – These systems oversee network traffic for any unusual behavior and may take measures to block or alert on potential threats. Encryption – Data transmitted over the network is encrypted to thwart unauthorized individuals from intercepting and deciphering it. Access Control – Access to the network is restricted to authorized users and devices, which involves identity verification and permission management.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – VPNs
facilitate secure remote access to a network by establishing an encrypted
connection, ensuring that data shared over public networks remains
confidential. Security Patches and Updates – Regular updates to network
hardware and software are essential to address vulnerabilities and prevent
exploitation by malicious actors. By adopting these measures, organizations can
shield their networks from external threats, reduce the likelihood of data
breaches, and uphold the security and integrity of their operations.
What is Cybersecurity and how to save from us
Cybersecurity is defined as the discipline focused on
safeguarding systems, networks, devices, and information from digital threats,
unauthorized access, or harm. Such cyber threats typically seek to gain access
to, alter, or eliminate sensitive data, extort financial resources from
individuals, or disrupt standard business operations. The field of
cybersecurity encompasses a range of methods, strategies, and tools aimed at
protecting against these risks.
Network
Security: Protecting the Integrity of Networks from Unauthorized Access and
Attacks
Network Security: Safeguarding Network Integrity Against Unauthorized Access and Attacks Network security encompasses the methodologies and technologies employed to protect the framework of a network, which includes the devices, data, and users associated with it. The primary objective is to defend the network against unauthorized access, cyber threats, and various risks that may jeopardize the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the network and its information. Essential Components of Network Security: Firewalls A firewall serves as a protective barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet.
It regulates incoming and outgoing traffic according to established security protocols. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) – These systems oversee network traffic for any unusual behavior and may take measures to block or alert on potential threats. Encryption – Data transmitted over the network is encrypted to thwart unauthorized individuals from intercepting and deciphering it. Access Control – Access to the network is restricted to authorized users and devices, which involves identity verification and permission management.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) – VPNs facilitate secure remote access to a network by establishing an encrypted connection, ensuring that data shared over public networks remains confidential. Security Patches and Updates – Regular updates to network hardware and software are essential to address vulnerabilities and prevent exploitation by malicious actors. By adopting these measures, organizations can shield their networks from external threats, reduce the likelihood of data breaches, and uphold the security and integrity of their operations.
Information Security: Ensuring the
Confidentiality and Integrity of Sensitive Data
In the contemporary digital landscape, where data serves as a crucial asset for enterprises, governmental bodies, and individuals alike, the significance of information security has escalated dramatically. Information security, commonly referred to as InfoSec, encompasses the strategies and practices aimed at shielding sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, modification, or destruction.
The core aims of information security include the preservation of confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data—collectively termed the CIA Triad. These principles are fundamental to the development of robust data protection strategies and are vital for sustaining trust, ensuring compliance, and maintaining operational security.The CIA Triad: Fundamental Elements of Information Security
Confidentiality
Definition: Confidentiality guarantees that sensitive
information is accessible solely to authorized personnel or systems. It acts as
a barrier against unauthorized access, thereby safeguarding personal,
corporate, and governmental data from being viewed or compromised by malicious entities.
Methods to Ensure Confidentiality: -
·
Encryption: A highly effective approach to
maintaining confidentiality is through encryption, which transforms data into a
coded format that can only be deciphered by individuals possessing the correct
decryption key.
·
Access Control: Implementing robust access
control measures is crucial. These measures ensure that only authorized users
can access specific data according to their roles and responsibilities. This
may involve password protection, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and
biometric verification.
·
Data
Masking: Data masking conceals sensitive information, such as credit card
numbers or Social Security numbers, from unauthorized users by replacing or
obscuring it while preserving its usability for those who require access.
·
Data Classification: Organizations classify data
according to its sensitivity (e.g., public, confidential, secret). By assigning
appropriate security levels to each classification, they can enhance the
protection of confidential information.
·
Least
Privilege Principle: This principle mandates that individuals are granted only
the essential level of access required to fulfill their job responsibilities.
By restricting access, organizations can mitigate the risks associated with
data breaches and insider threats.
·
Real-World Example: In the healthcare sector,
maintaining the confidentiality of patient information is vital for adhering to
regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
(HIPAA). Healthcare institutions implement encryption and access control
measures to safeguard electronic health records (EHRs) from unauthorized access
Integrity
Definition: Integrity
pertains to safeguarding data against unauthorized modifications or tampering.
It guarantees that information remains accurate, consistent, and reliable
throughout its entire lifecycle. The primary objective is to ensure that data,
whether in storage or transit, is not maliciously or inadvertently altered,
thus preserving its intended state.
Methods to Ensure Integrity
·
Hashing: This process involves generating a
unique "digital fingerprint" of data, known as a hash value, through
the use of algorithms. Any alteration to the data will result in a change in
the hash value, thereby notifying users of potential tampering.
·
Checksums and Cyclic Redundancy Checks (CRCs):
These methods are employed to identify changes or errors in data during
transmission. A discrepancy between the checksum or CRC value at the receiving
end and that of the sender indicates that the data has been compromised during
transit.
·
Digital Signatures: Utilizing encryption and
hashing, digital signatures verify the authenticity of data and confirm that it
has not been altered. They are commonly employed in electronic communications,
contracts, and software distribution.
·
Version Control: Organizations handling
substantial amounts of data, particularly in software development or research,
utilize version control systems to monitor changes made to files, thereby
ensuring data integrity over time.
·
Audit Trails: Maintaining records of data
access, modifications, and transfers assists organizations in identifying and
preventing unauthorized alterations. These logs are also valuable for forensic
analysis in the event of security breaches.
· Real-World Example: In the financial industry, preserving the integrity of transaction records is vital for preventing fraud and inaccuracies. Financial institutions employ digital signatures and hashing techniques to ensure the precision of transaction data.
Availability
Definition: Availability refers to the assurance that data and information systems are accessible to authorized users whenever required. Although availability is not directly linked to confidentiality and integrity, it is a vital component of information security. If availability is compromised, even the most secure systems may become ineffective during crucial periods.
· Methods to Ensure Availability:
· Redundancy: The implementation of redundant
systems guarantees that in the event of a system failure, a backup can
seamlessly take over, thereby minimizing downtime.
· Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Planning: Establishing a comprehensive plan for data recovery following a
disaster or cyber incident is essential for ensuring minimal disruption and
swift restoration of data and services.
· DDoS Protection: Distributed Denial of Service
(DDoS) attacks can incapacitate systems, rendering them unavailable. Utilizing
DDoS protection tools and services is critical to prevent or lessen the effects
of such attacks.
· Data Backups: Conducting regular backups is
crucial for recovering data that may be lost due to system failures or
cyberattacks. These backups should be securely stored in geographically diverse
locations.
· High Availability Architectures: These
architectures employ load balancing, failover systems, and scalable
infrastructure to guarantee that essential services remain functional, even
during peak demand or unforeseen outages.
· Real-World Example: E-commerce platforms must
maintain 24/7 availability, particularly during high-traffic shopping periods
such as holidays. High availability systems ensure that even in the event of a
server failure, customers can continue to complete transactions without any
interruptions.
·
Ensuring Online Safety: Essential Cybersecurity
Guidelines for 2024
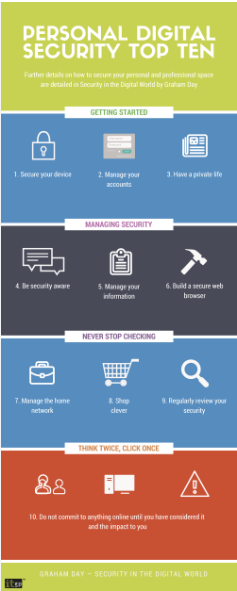
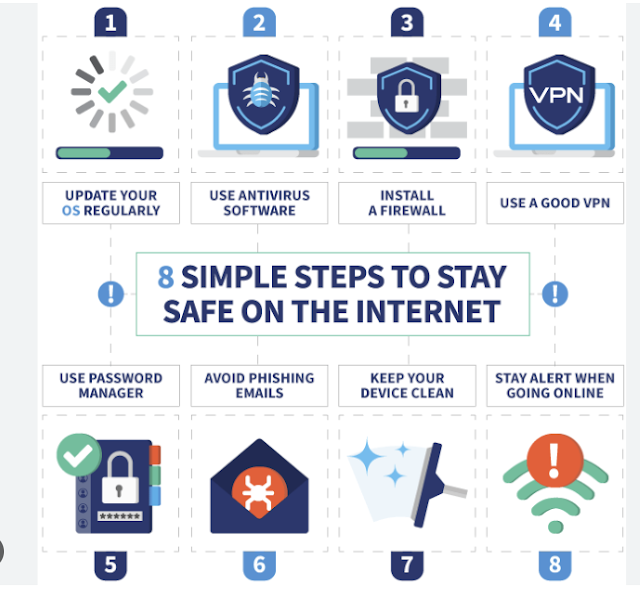
As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity, it is crucial to adopt proactive strategies for online safety. Below are the essential cybersecurity guidelines for 2024:
·
Create Strong, Distinct Passwords
Rationale: Weak passwords are among the simplest methods for
attackers to infiltrate accounts.
Recommendation: Develop complex passwords that incorporate a
mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. Refrain from reusing passwords across
different platforms.
Additional Tip: Consider utilizing a password manager to securely store and generate robust passwords.
·
Activate Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Rationale: Even if a password is compromised, access to
accounts remains blocked without the second authentication factor.
Recommendation: Implement 2FA wherever feasible, particularly for email, banking, and social media accounts.
·
Exercise Caution Against Phishing Scams
Rationale: Phishing scams deceive users into divulging
sensitive information by masquerading as trustworthy entities.
Recommendation: Steer clear of clicking on dubious email links or downloading attachments from unfamiliar sources. Always confirm the legitimacy of the source before sharing personal details.
·
Regularly Update Software
Rationale: Software updates frequently include fixes for
security vulnerabilities.
Recommendation: Ensure that your operating system, applications, and antivirus software are consistently updated to safeguard against the latest threats.
·
Utilize a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Rationale: VPNs encrypt internet traffic, concealing online
activities from hackers and surveillance.
Recommendation: Employ a reputable VPN to maintain data privacy, particularly when accessing public Wi-Fi networks.
·
. Maintain Data Backups
Rationale: In the event of a ransomware attack or data loss,
backups can facilitate the recovery of essential files.
Recommendation: Establish a routine for backing up important data to cloud storage or external hard drives.
·
Remain Vigilant on Public Wi-Fi
Rationale: Public Wi-Fi networks are more susceptible to
cyberattacks, increasing the risk of data interception by hackers.
Recommendation: Avoid logging into sensitive accounts (such
as banking) on public networks. If necessary, always utilize a VPN.
·
Install Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Rationale: These applications offer an essential layer of protection by
identifying and eliminating harmful software. Recommendation: opt for
well-regarded antivirus solutions and arrange for routine system scans.
·
Monitor
Your Accounts for Suspicious Activity Rationale: Cybercriminals frequently
exploit stolen information to execute unauthorized transactions or
modifications. Recommendation: Consistently review your bank accounts, emails,
and social media platforms for indications of unauthorized access.
· Educate Yourself About the Latest Threats Rationale: Cybersecurity threats are constantly changing, and being well-informed enables you to identify potential dangers. Recommendation: Keep up with cybersecurity news, subscribe to notifications from reliable sources, and engage in training sessions or webinars focused on cyber awareness.
conclusion
information security is a continuous endeavor that
necessitates an integration of technology, policy, and user education to
protect sensitive information. By following the tenets of the CIA
Triad—confidentiality, integrity, and availability—and establishing strong
security protocols, organizations can significantly diminish the likelihood of
data breaches and other security challenges. Furthermore, it is essential to
recognize and address the evolving threats posed by malware, phishing, and
social engineering to ensure the protection of information in an increasingly
interconnected environment. As the value of data escalates and cyber threats
become more advanced, the significance of information security will only
intensify, requiring ongoing vigilance and innovation in security
methodologies.
Information
Security
Safeguarding the Confidentiality and Integrity of Sensitive
Information
·
Information security encompasses the
safeguarding of sensitive information against unauthorized access, disclosure,
modification, or destruction. The fundamental principles, collectively referred
to as the CIA Triad, include:
·
Confidentiality – Guaranteeing that only
authorized personnel have access to the information. Techniques employed
include encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication.
·
Integrity – Ensuring that data remains unaltered
by unauthorized parties. Approaches such as hashing, digital signatures, and
audit trails are utilized to maintain data accuracy and dependability.
·
Availability – Making certain that data and
systems are accessible when required. Strategies like backup systems, disaster
recovery plans, and redundancy measures are implemented to ensure
availability.
The importance of information security lies in its role in preventing cyber threats, protecting individual privacy, and adhering to regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Endpoint
security
serves to safeguard devices such as computers, smartphones,
and tablets against cyber threats. It achieves this protection by utilizing
various tools, including antivirus software, firewalls, and encryption methods.
By securing each endpoint, it plays a crucial role in preventing unauthorized
access and data breaches within a network.
Application
security
safeguards software against cyber threats by detecting and
rectifying vulnerabilities, thereby ensuring the secure and safe utilization of
applications. Cloud security defends data, applications, and services hosted in
the cloud through measures such as encryption, access controls, and continuous
threat monitoring, thereby maintaining safety and privacy.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
regulates access to
systems and data within an organization. This process encompasses the
management of user identities, the establishment of permissions, and the
enforcement of policies to guarantee that only authorized personnel can access
designated resources. IAM systems are instrumental in preventing unauthorized
access and safeguarding sensitive information by employing authentication
techniques, including passwords and multi-factor authentication.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
are
essential elements of an organization's risk management framework, aimed at
guaranteeing the continuation of operations and the safeguarding of data during
and following unforeseen disruptions. Disaster recovery emphasizes the
methodologies and technologies necessary to reinstate IT systems and data after
significant incidents, such as natural disasters, cyberattacks, or system
failures. This process entails the development and routine testing of backup
strategies, the establishment of data recovery protocols, and the assurance of
critical infrastructure availability. Conversely, Business Continuity focuses
on the planning and strategies required to sustain vital functions and reduce
downtime during a disruption. This encompasses the implementation of
alternative workflows, communication strategies, and temporary operational
arrangements to ensure the organization operates effectively. Collectively,
disaster recovery and business continuity enable an organization to promptly
rebound from adverse events while preserving its essential operations and
services.



.jpg)









.jpg)



No comments:
Post a Comment